
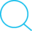
To distribute work across clusters and reduce the memory requirements of each node, Spark will split the data into smaller parts called Partitions. Each of these is then sent to an Executor to be processed. Only one partition is computer per executor thread at a time, therefore the size and quantity of partitions passed to an executor is directly porportional to the time it takes to complete.
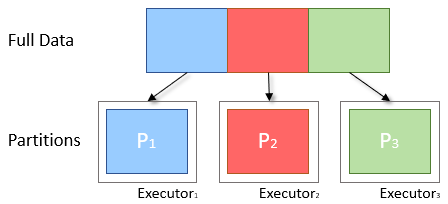
Data is often split by a key, if the split is not even, then one partition may end up having more or less data than the others.
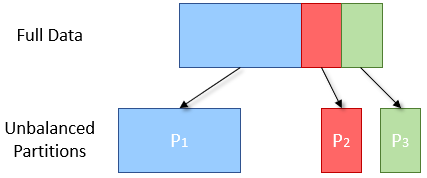
If the data are splitted into too few partitions, some executor may become idle
By increasing the number of partitions used for computation, the performance can be increased as each executor will have similar amount of work to do without data skew or schedling problem.
A Shuffle occurs when data is rearrange between partitions. This is required when a transformation requires information form other partitions, like summing all values in a column. Spark will father the required data from each partition and combine it into a new partition, likely on a different executor.
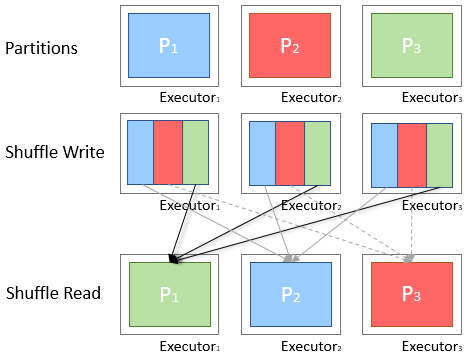
During a shuffle, spark writes data to disk and transform them across the network, this will stop processing the data in-memory and causing performance bottleneck. So try reduce the number of shuffling or reduce the amount of data bring shuffled.
Before shuffling the data, it is prefered to combie the value in the current partitions and pass that aggregated value to shuffle, which is called Map-Side Reduction
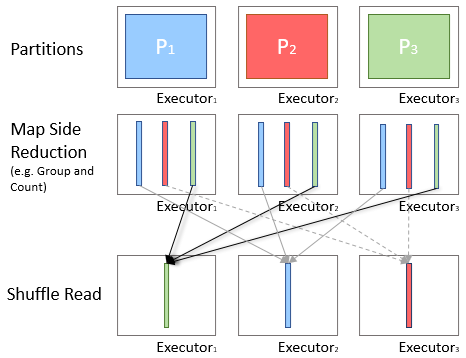
Spark groupBy function will perform map-side reduction automatically where possible.
This is an optimization technique in which saves the result of RDD evaluaton. By calling cache() or persist(), the RDD is stored in-memmory, which can be used efficiently across parallel operations.
Action takes RDD, and returns a value to the Driver program
Spark Transformation builds lineage among RDDs, also known as RDD operator grah or RDD depdency graph. The transformations are lazy, meaning they are not executed until we call the action. Transformation takes a RDD, turns to another RDD
Narrow Transformation - all the data required to compute the records are in a single partion

Wide Transformation - elements required are in many paritions

Yarn: each Spark executor runs as a Yarn container, spark can host multiple tasks within the same container, which saves startup time.
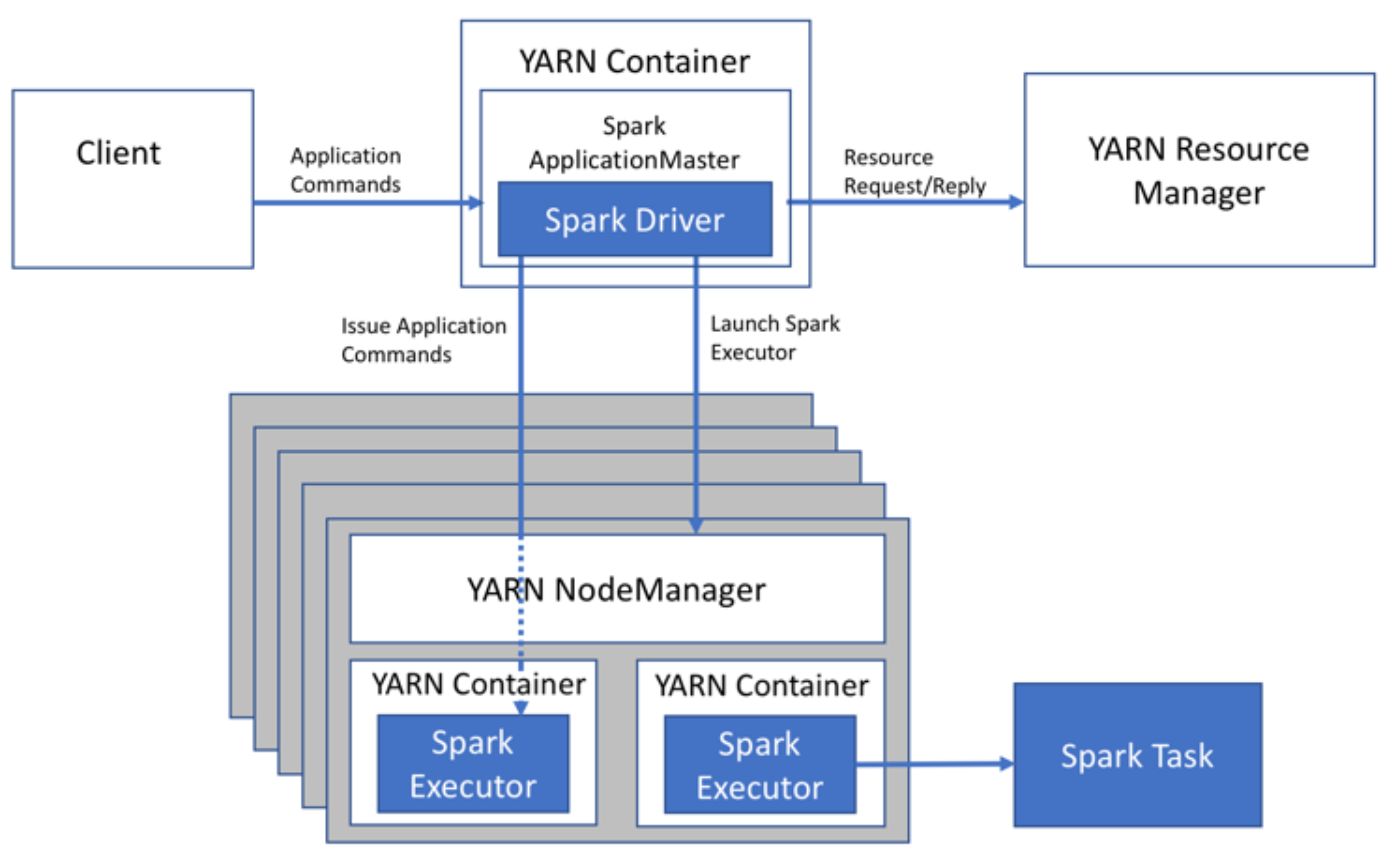
Spark Cluster vs Standalone:

Spark Context: the entry gate of Spark functionality, allowing application to access the spark cluster with resource manager. 
Cluster: A number of worker nodes
Worker: a Worker node has a finite or fixed number of Executors allocated.
Executor: distributed agent in responsible of executing tasks
RDD: Resilient Distributed Dataset, RDD contains Partition contains Rows
DAG: moels the dependency of the RDD
Stage: A steps in the physical execution plan, a set of parallel tasks; in other words, each job which gets divided into smaller sets of task is a stage.
