Hadoop Distributed File System - HDFS, is a distributed files system that allows big data to be stored across multiple nodes.
Yarn is the resource management in hadoop that allows multiple processing engines to manage data in a single platform.
Key Features of HDFS
HDFS Architecture: (Master-slave)

RDBMS vs Hadoop
| RDBMS | HDFS | |
|---|---|---|
| Data Types | RDBMS relies on the structured data and the schema of the data is always known. | Any kind of data can be stored into Hadoop i.e. Be it structured, unstructured or semi-structured. |
| Processing | RDBMS provides limited or no processing capabilities. | Hadoop allows us to process the data which is distributed across the cluster in a parallel fashion. |
| Schema on Read Vs. Write | RDBMS is based on ‘schema on write’ where schema validation is done before loading the data. | On the contrary, Hadoop follows the schema on read policy. |
| Read/Write Speed | In RDBMS, reads are fast because the schema of the data is already known. | The writes are fast in HDFS because no schema validation happens during HDFS write. |
| Cost | Licensed software, therefore, I have to pay for the software. | Hadoop is an open source framework. So, I don’t need to pay for the software. |
| Best Fit Use Case | RDBMS is used for OLTP (Online Trasanctional Processing) system. | Hadoop is used for Data discovery, data analytics or OLAP system. |
Problem with Small Files:
Block: these are the smallest continuous location on the hard drive where data is stored, hdfs store each files as blocks and distributed it across the hadoop cluster; by default it’s size is 128 MB

Replication: blocks of data are also replicated to provide fault tolerance, so even when a DataNode fails or a data block gets corrupted, the data can still be retrieved
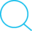
HDFS Write:
Client reachout to NameNode for request to writting to two blocks
NameNode gives a list of IP adress for the DataNode (all replicates)
The block will also be copied to these three DataNodes